Considera gli esempi del libro di testo a pagina 198 e successive.
Lo pseudolinguaggio è tradotto in Python.
1
print("n = ") # costo=1
n = int(input()) # costo=1
i = i+1 # costo=1
T(n) = 1+1+1 = 3
Per semplificare i calcoli associamo alle tre istruzioni un costo unitario ma in realtà hanno tempi d’esecuzione molto diversi
- istruzione di output (
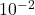 s)
s) - istruzione di input (1 s)
- addizione e assegnazione (
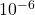 s)
s)
2
print("n = ") # c1
n = int(input()) # c2
i = 1 # c3
somma = 0 # c4
while(i <= n): # c5
somma = somma+i # c6
i = i+1 # c7
print("La somma dei primi", n, "numeri è", somma) # c8
T(n) = ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
3.1
if(y > 0): # c1
r = 1 # c2
z = 2 # c3
Se l’if(...) ha successo: ![]()
Se l’if(...) fallisce: ![]()
Quindi: ![]()
3.2
if(y > 0): # c1
r = 1 # c2
else:
z = 2 # c3
p = 0 # c4
r = 2 # c5
Se l’if(...) ha successo: ![]()
Se l’if(...) fallisce: ![]()
Quindi: ![]()
4
def Somma(x, y):
s = x+y # f1
return s # f2
print("n = ") # c1
n = int(input()) # c2
i = 1 # c3
somma = 0 # c4
while(i <= n): # c5
somma = Somma(i, somma) # c6 c7
i = i+1 # c8
print("La somma dei primi", n, "numeri è", somma) # c9
T(n) = ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
5
if(x > 0): # c1
if(y > 0): # c2
r = 1 # c3
else:
r = 2 # c4
t = 1 # c5
z = 3 # c6
Se …: ![]()
Se …: ![]()
Se …: ![]()
Quindi: ![]()
6
i = 0 # c1
while(i < n): # c2
i = i+1 # c3
Se i = 0..(n-1) allora il while si ripete n volte.
T(n) = ![]() =
= ![]() =
= ![]()
7
Il costrutto repeat ... until ... non è presente in Python
8
L’istruzione originale for è tradotta in while per evidenziare le singole istruzioni
def SommaNumeriPari(n):
m = 0 # c1
i = 1 # c2
while(i <= n): # c3
p = 2*i # c4
m = m+p # c5
i = i+1 # c6
return m # c7
T(n) = ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
9
Attenzione: il limite del ciclo while è ![]()
i = 0 # c1
while(i < 2*n): # c2
i = i+1 # c3
j = j*3+4367 # c4
T(n) = ![]() =
= ![]() =
= ![]() =
= ![]()
10
L’istruzione originale for è tradotta in while per evidenziare le singole istruzioni.
i = 0 # c1
while(i < n): # c2
j = 1 # c3
while(j <= n): # c4
print("CIAO") # c5
j = j+1 # c6
i = i+1 # c7
Se i = 0..(n-1) allora il while esterno cicla n volte.
Se j = 1..n allora il while interno cicla n volte.
Il messaggio CIAO verrà visualizzato ![]() volte
volte
T(n) = ![]() =
= ![]()
= ![]() =
= ![]()
= ![]() =
= ![]()
= ![]() =
= ![]()
11
Le istruzioni originali for sono tradotte in while per evidenziare le singole istruzioni
def Funzione(n, m):
x = 0 # c1
i = 1 # c2
while(i <= n): # c3
j = 1 # c4
while(j <= m): # c5
x = x+1 # c6
y = x # c7
j = j+1 # c8
i = i+1 # c9
return x # c10
Il while esterno cicla n volte.
Il while interno cicla m volte
T(n) = ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()
= ![]()